My body.
How does my brain work?
The Human Brain is incredibly complex organ which controls our thoughts and emotions, physical movement, and all the different processes which regulate our body. The brain and spinal cord form a system called the Central Nervous System (CNS), and it is thorough this network of nerves that all the information in our body travels.
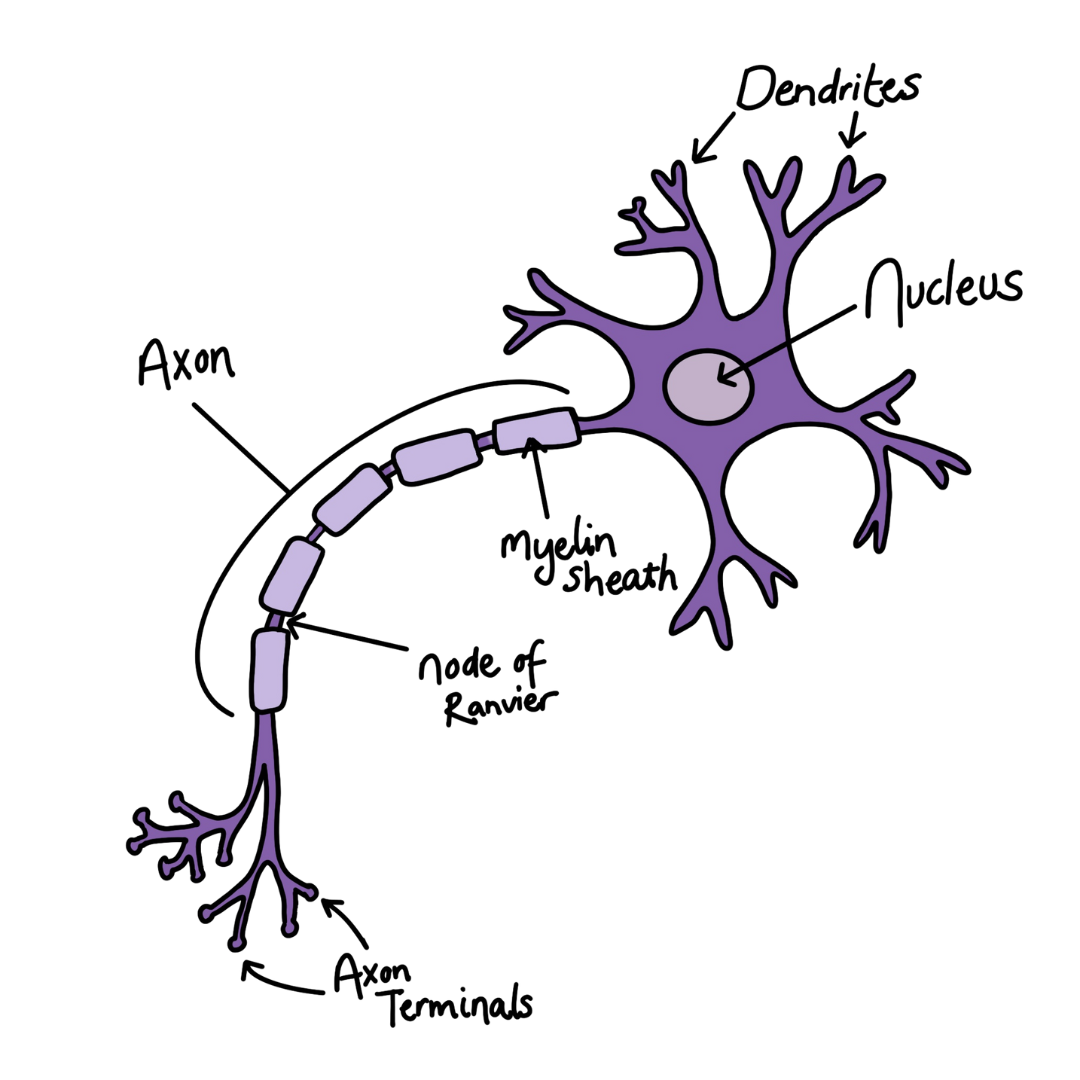
Nerve cells are specially adapted to be long and thin, with lots of connections, speeding up the transfer of information. The dendrites around the cell body act as connection points to other nerve cells, allowing the electrical signal to move along the long, thin axon, to the end of the cell where it connects to the next nerve cell. This creates a vast network throughout our body.
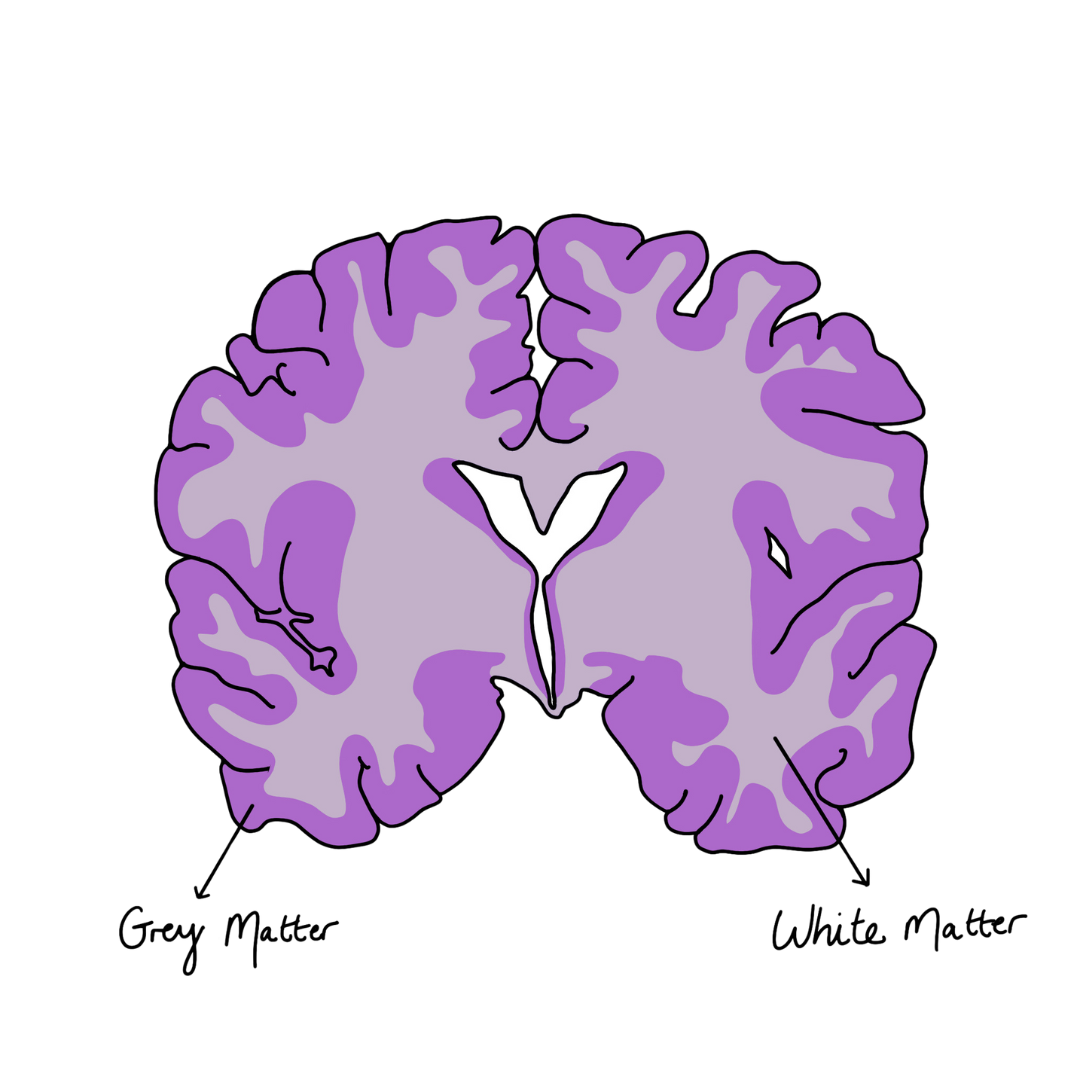
The Brain itself is made up of both grey and white matter - the grey matter is a darker portion of brain tissue which sits on the outer section of the brain. It is primarily responsible for processing and interpreting information. The inside of the brain is known as white matter. This area transmits the information to other parts of the body. With these two different types of brain tissue, the brain is able to send and receive chemical and electrical signals. It is this that allows the brain to control so many bodily processes.
This video from Operation Ouch shows you what a REAL human brain looks like.
If we look at the brain in more detail, we would see that it is made up of multiple regions, each with a specific role to play in coordinating the human body.
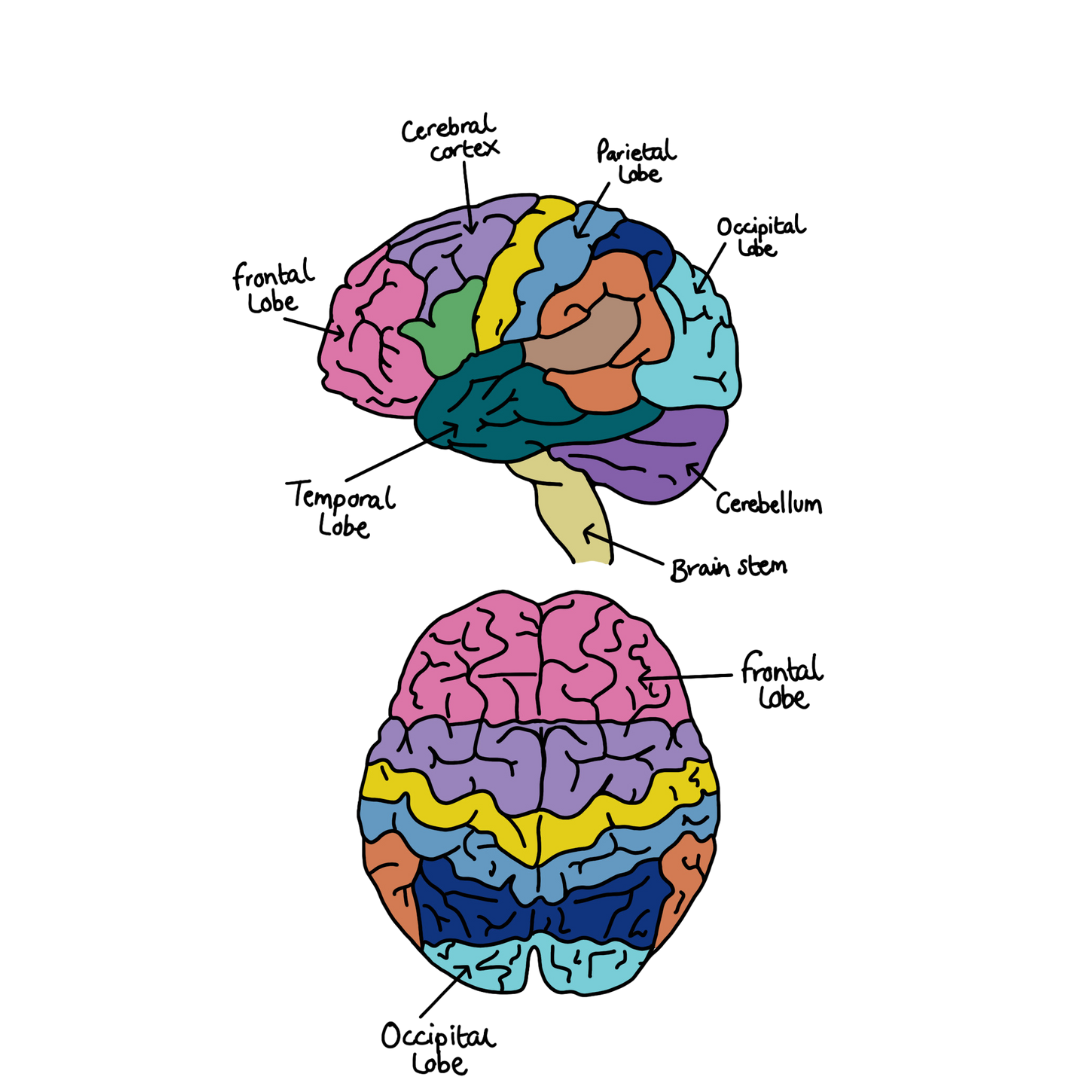
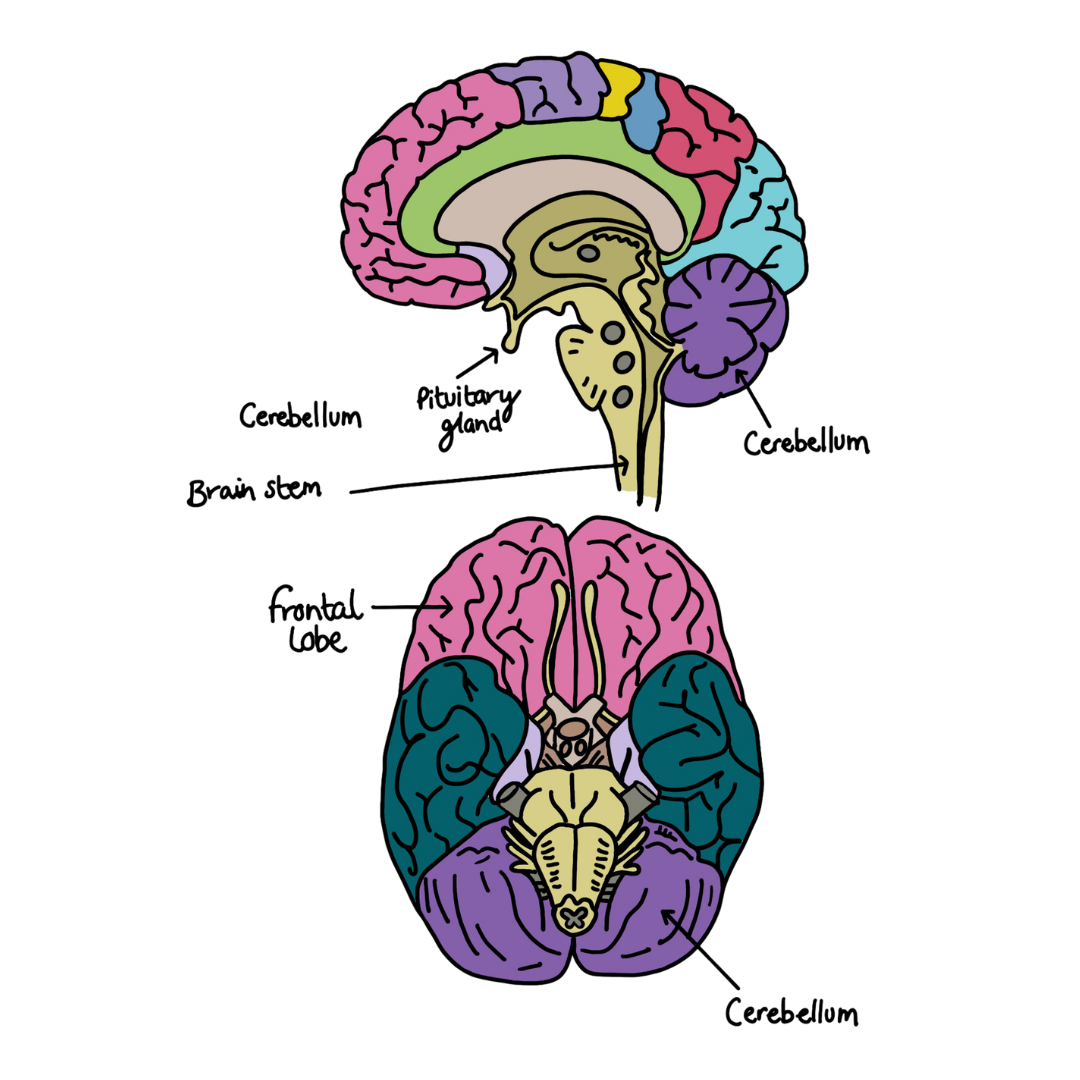
Brain Strucure
Frontal Lobe - The largest area of the brain, this area is involved in decision making, personality and movement. It also contains a region which is associated with speech.
Cerebral Cortex - This region is divided into two halves covered in ridges and folds, which provide a large surface area. The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body, and the left hemisphere controls the right side of the body. Both halves are able to communicate to one another. This area is associated with coordinating movement, regulating temperature, thinking and problem-solving, as well as emotions and learning.
Parietal Lobe - This region is found in the middle of the brain and is associated with identifying objects and understanding spatial awareness. It is also involved in interpreting pressure (touch) and pain, as well as understanding spoken language.
Occipital Lobe - This region is associated with vision.
Cerebellum - This region is a fist-sized part of the brain which is found at the base of the skull. It’s role is to coordinate voluntary muscle movements and to maintain balance and posture.
Pituitary Gland - This glad regulates hormones, the chemical signals within the body, coordinating glands such as the thyroid, adrenals and ovaries.
Temporal Lobe - This region is associated with speech and short-term memory.
Brain Stem - A complex area which connects to the spinal cord.
This video from National Geographic explores some of these key regions of the brain and the roles they play in coordinating our bodies.
Ready to Dive Deeper?
This video from Crash Course goes into more depth, exploring the different structures of the brain, how they develop and how information is transfered between these areas. If the biology of the brain has sparked your interest, this is for you!
A Million Things To Ask A Neuroscientist
This book from Dr Mike Tranter explains more about the neurology of the brain by answering questions sent to him by the public. He talks about some of the mysteries of the brain, and how the field of neuroscience might change in the future.